Heating, Ventilation and Air conditioning
HVAC is the technology of indoor and vehicular environmental comfort. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality depending on the inputs of the operator as well as electronic sensors. It is the process of "exchanging" or replacing air in any space to provide high air quality which involves temperature control, oxygen replenishment, and removal of moisture, odors, smoke, heat, dust, airborne bacteria, and carbon dioxide. Ventilation removes unpleasant smells and excessive moisture, introduces outside air, keeps interior building air circulating, and prevents stagnation of the interior air.
Components of a Basic HVAC System
1. Cabin Air Filter

2. Heater Blower/Blower Motor
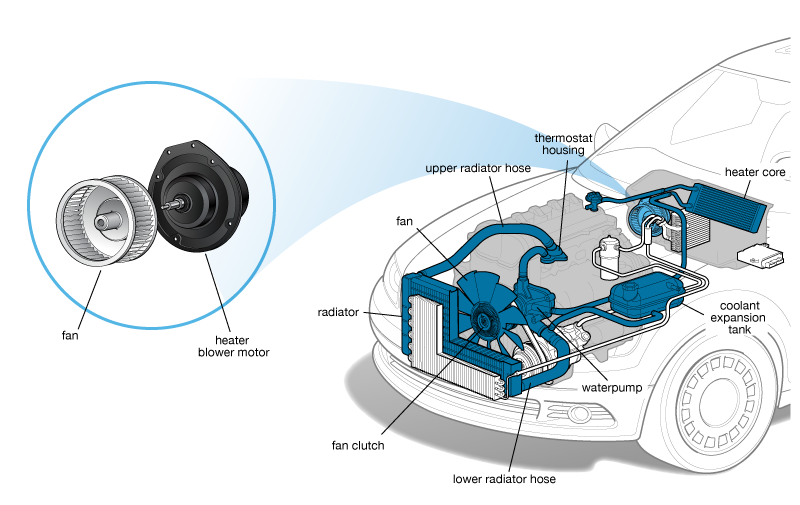

3. Heater Core
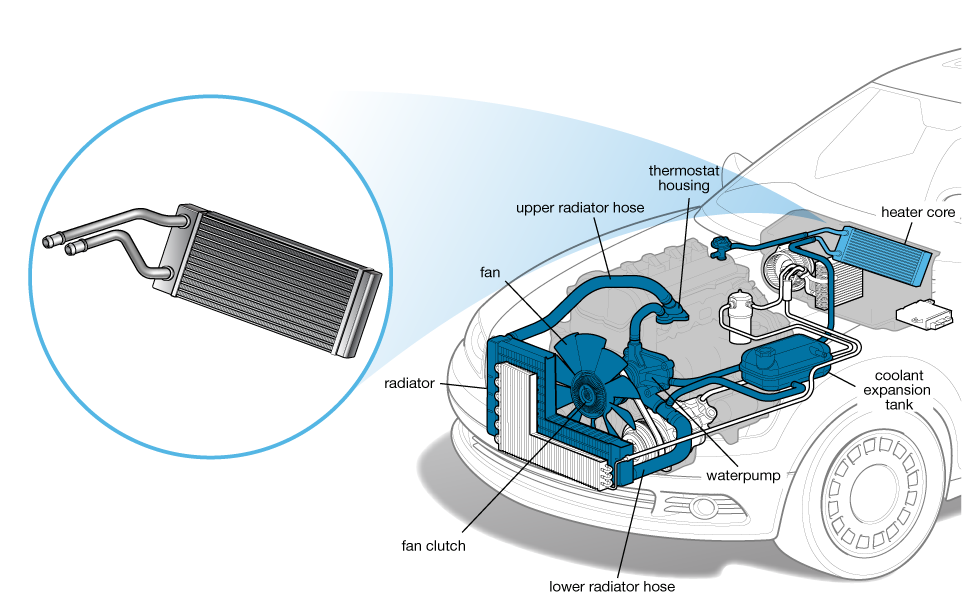

Heater shutoff valve
The heater shutoff valve blocks the flow of coolant through the heater core when the A/C system is set to A/C max or the temperature control is set to it’s coldest position.


4. Evaporator Core

The air-conditioning evaporator is a small radiator inside the dashboard that provides cold air for the air-conditioning system. It’s called the evaporator because it’s where the freezing liquid refrigerant takes on any heat from the air blown through it and changes into a gaseous state (evaporating it) before returning it to the air-conditioning condenser to shed the heat; the process is constantly repeated. The air that emerges from the air conditioner is cold as a result.
5. Evaporator Drain

6. Mode Doors

 |
| a) flow through upper vents b) floor vents c) flow through defogger vents |
7. Blend Door
The
blend door is not much different than the mode doors except it controls
how much air passes through the heater core. The more air that passes
through the heater core, the warmer the air will be at the vents. A
blend door moves to vary the amount of air passing through the vehicle’s
heater core. The blend door is controlled by a blend door actuator,
which can be a cable or an electric motor.
Controlling the Doors
1. Cable Style
Cable style is by far the most simple as well as the most reliable system. They are usually found on older base model vehicles but some newer midrange manufacturers still use this system for its reliability. Cables are attached to the heater control knobs, which open and close the mode and blend doors to achieve the air flow desired. The blower motor, A/C compressor engagement and recirculation flap may still be electronically controlled. Cable systems are generally the most reliable but they are not the most convenient. These systems usually do not have any sensors other than the sensors normally found in all A/C systems.
1. Cable Style
Cable style is by far the most simple as well as the most reliable system. They are usually found on older base model vehicles but some newer midrange manufacturers still use this system for its reliability. Cables are attached to the heater control knobs, which open and close the mode and blend doors to achieve the air flow desired. The blower motor, A/C compressor engagement and recirculation flap may still be electronically controlled. Cable systems are generally the most reliable but they are not the most convenient. These systems usually do not have any sensors other than the sensors normally found in all A/C systems.

2. Vacuum Actuated
Vacuum actuated systems use engine vacuum to open and close the blend, mode and recirculate doors. A vacuum hose from the engine intake manifold comes through the firewall and into the cabin. Engine vacuum is redirected to the appropriate actuator to control the doors and airflow, based on the operators request. This system may still requires to make corrections to the air temperature or it may have an auto feature that will maintain a set cabin temperature. It may still need to be turned the A/C on or off manually. One of the serious downsides to this system is the complex vacuum routing under the dash. Over time the vacuum lines can leak and cause poor idle or other drive-ability problems because now the engine is pulling in unmetered air. It can be tricky to find these leaks.
Stepper Motor
These systems are fully electronic, and almost always have a automatic temperature regulating feature. Simply put, a stepper motor is an electronically controlled motor that can move to a fine tuned degree of rotation and hold. They use a series of sensors to decide at what temperature, and how hard to blow the air into the cabin. These systems usually use a PWM (pulse width modulation) variable speed heater blower to better control air flow. The mode doors can still be left up to the operator even in auto mode. The electronic stepper motors may be attached to the doors themselves or be connected by a cable or lever. One problem with this system in the past was the placement of the cabin air temperature sensor. If the sensor is near the drink holder, the system would supply full cold in the middle of winter or the system would supply with as much heat as it can give. This is no longer a problem on modern systems, modern systems use multiple cabin air temperature sensors and place them away from anything that may skew readings.
These systems are fully electronic, and almost always have a automatic temperature regulating feature. Simply put, a stepper motor is an electronically controlled motor that can move to a fine tuned degree of rotation and hold. They use a series of sensors to decide at what temperature, and how hard to blow the air into the cabin. These systems usually use a PWM (pulse width modulation) variable speed heater blower to better control air flow. The mode doors can still be left up to the operator even in auto mode. The electronic stepper motors may be attached to the doors themselves or be connected by a cable or lever. One problem with this system in the past was the placement of the cabin air temperature sensor. If the sensor is near the drink holder, the system would supply full cold in the middle of winter or the system would supply with as much heat as it can give. This is no longer a problem on modern systems, modern systems use multiple cabin air temperature sensors and place them away from anything that may skew readings.
Working
The re-circulation flap, it determines whether air for the HVAC system is taken from outside the cabin or recirculated air from the cabin. Outside air has to pass through a cabin air filter before making its way into the rest of the HVAC system. Outside air is usually taken from under the wiper cowl.
Next is the blower motor, this determines how hard to blow air into the cabin. After that air passes through the A/C evaporator. The evaporator core does not absorb heat/cool the air unless the compressor is activated, therefore the evaporator does not need to be bypassed when the A/C is not in use. From there the air comes to the blend door.

Possible Settings
1. Full Heat

In this setting the operator has demanded full heat. 100% of air flow is directed through the heater core by the blend door to deliver the most heat possible to the main upper vents.
In this setting the operator has selected full cold but has left the A/C off by either selecting economy mode or by not selecting A/C on. 100% of the air flow is directed around the heater core to allow filtered air at ambient temperature to enter the cabin through the main upper vents.
2. Max A/C

In this setting the operator has selected max A/C. The A/C compressor engages and the evaporator begins to absorb heat. To get the most cooling power, the HVAC system takes air from the cabin that has already been cooled once and cools it again instead of trying to cool hot ambient air.
3. Economy Mode
In this setting the operator has selected full cold but has left the A/C off by either selecting economy mode or by not selecting A/C on. 100% of the air flow is directed around the heater core to allow filtered air at ambient temperature to enter the cabin through the main upper vents. In some cases A/C is not required to provide adequate cooling. Without the A/C compressor running the vehicle will get noticeably better fuel economy.
Outside Rear View Mirror(ORVM)
A wing mirror, also known as the fender mirror, door mirror, outside rear-view mirror or side view mirror, is a mirror found on the exterior of motor vehicles for the purposes of helping the driver to see areas behind and to the sides of the vehicle, outside the driver's peripheral vision (in the 'blind spot').

Classification:
- Internally Adjustable
- Manual
- Electrical
- Externally adjustable
- Manual
Internally adjustable ORVM means there can be a manual handle/joystick near the window by which the mirror position can be adjusted (without moving hands outside and physically adjusting)
Manual Electronic Outside Rear View Mirror. A conventional power mirror switch is essentially two rocker switches built into a single housing. Each rocker switch is connected to two wires that are connected to a reversible DC (direct current) motor inside the side view mirror on either door. Each rear view mirror has two DC motors. One DC motor operates the up/down function while the other DC motor operates the left/right function.



Memory Function : The mirrors work in conjunction with the adjustment of seats. Different drivers have different driving adjustments with the seating and hence the seats are provided with memory function. Once the desired setting is pressed, the seats adjust automatically as per the drivers requirement, along with the exterior mirrors which are synchronized with the seat adjustment.

Heating : As we all know the rear windscreen comes with rear demister to remove mist and to give clear visibility to driver for rear viewing, nowadays even the ORVM come with heating feature which responds automatically to the changes in the humidity level and the temperature, especially in the rainy and winter seasons. Even the side view of car is clear now.


Automatic Anti Glare : Exterior mirrors are now fitted with light-sensitive semiconductors, which turn light into current. These sensors are attached to a microprocessor that can detect glare from headlights and send a charge through the electrochromic material( tungsten oxide,titanium dioxide)(An electrochromic material changes colour when charged by an electrical current. Send voltage through it, and it darkens. Remove the voltage, and it lightens. This is largely a chemical reaction that is kicked off by adding electricity.) to respond to this input. As mentioned, the system responds to the amount of light present. The more intense the glare, the more the mirror will darken. The mirror itself consists of two layers of glass with a layer of gel in between, which is where the electrochromic material resides. Add light (and consequently voltage), and the gel darkens. Take it away, and it lightens.


Automatic Tilt : When the driver shifts the gear to reverse the side mirror automatically tilts downward to give driver proper visibility of the left hand side while reversing. The driver car have a view of the roadside to rear left wheel to park the car conveniently in tight parking situations. when the car is locked, the mirrors get retracted automatically to save itself from any mishap by other vehicle when parked and open it when the engine is turned on.
Direction Indicator Mirrors: While the vehicle is running, the forward-facing portion of the appropriate mirror housing blinks when the direction indicator is switched on.
 Puddle Lamps:The lamps on the bottom part of the mirror housing light when we use the transmitter to unlock the doors or when the door is opened.
Puddle Lamps:The lamps on the bottom part of the mirror housing light when we use the transmitter to unlock the doors or when the door is opened.

Rain Sensing Wiper System
Rain sensing wipers are the windscreen wipers which come into action automatically when they sense water on the windscreen of the vehicle.
Basic components

Rain sensing wipers employ an electronic control module fitted near the windscreen. It serves as the brain of this system. It uses optical sensors to detect the moisture. The sensor is mounted in contact with the inside of the windshield, near the rear view mirror.

 This reflected light generates a voltage in the electronic module. When the reflected light is more, it generates more voltage and vice versa. The electronic module is programmed in such a way that it activates the wiper motor when the generated voltage is less i.e. when it reflects very small light. The speed and time of activation of the wipers depends on the degree of wetness of the windscreen. ECM varies the voltage based on the input from rain sensor and runs the servo motor.
This reflected light generates a voltage in the electronic module. When the reflected light is more, it generates more voltage and vice versa. The electronic module is programmed in such a way that it activates the wiper motor when the generated voltage is less i.e. when it reflects very small light. The speed and time of activation of the wipers depends on the degree of wetness of the windscreen. ECM varies the voltage based on the input from rain sensor and runs the servo motor.
ECM sets the speed of the wipers based on how fast the moisture builds up between wipes. It can operate the wipers at any speed. The system adjusts the speed as often as necessary to match with the rate of moisture accumulation.

Environment Information System


Rain Sensing Wiper System
Rain sensing wipers are the windscreen wipers which come into action automatically when they sense water on the windscreen of the vehicle.
Basic components
- Rain sensor
- Microcontroller
- servo motor


The sensor projects infrared light into the windshield at a 45-degree angle. If the glass is clear, most of this light is reflected back into the sensor by the front of the windshield. If water droplets are on the glass, they reflect the light in different directions on the windshield, the infrared light beam passes through them instead of reflecting. So, the amount of light coming back to the sensor is very low, wetter the glass, the less light makes it back into the sensor.

 |
| Rack and pinion type |
 |
| Worm and wheel type |

Environment Information System
Environment Information System is that a space sensors system using laser, ultrasonic or radar sensors are installed in a highway environment and communication technology is used to realize the information exchange between the Highway Information server and vehicles, which provides vehicles with the surrounding road information. Considering the high-speed feature of vehicles on highways, when vehicles will be passing a road ahead that is prone to accidents, the vehicle driving state should be predicted to ensure drivers have road environment perception information in advance, thereby ensuring vehicle driving safety and stability. In order to verify the accuracy and feasibility of the Highway information server, a traditional vehicle-mounted sensor system for environment perception is used to obtain the relative driving state.

The system has four parts: the sensor nodes, base station, communication devices(connected with sink node) (laser, ultrasonic, radar, etc.) and wireless network and server systems. The distributed sensors are placed on road sides and sense the environment perception and send the information to sink sensor and then to the base station. After obtained the information sent to system servers and server evaluate the information and further disseminate the information to the vehicles. Servers are installed in traffic management centre (TMC) and collect all the data from sensors and further process the data and mathematical analysis.
The first server (S1) system is responsible to collect and process data and second server (S2) collect the data and effective information disseminate to vehicles. The distance and velocity data is acquired from sensors placed on highways. The vehicle driving states are collected from vehicle mounted sensor system, comparing both vehicle driving states and estimated errors between them and check the system performance. When vehicles are passing from highway the effective information collected through sensors and send the data to sink nodes and then send to base station and to the servers which are installed in traffic management center and after processing the data will be broadcasted to other vehicles through base stations.


Steering column is the piece that attaches the steering wheel to the internal steering mechanism of the vehicle.
conventional steering columnThe main disadvantage of having a conventional steering column is that, the steering wheel’s height and angle cannot be adjusted as per the Driver's need.
 The
Tilt mechanism which offers the driver to adjust the steering wheel in
different positions. The grooves in the Column and a Spring Adjusted
Lock Pin is there. The driver just has to release the pin and adjust it
according to his needs. As the name implies, in this mechanism we just
can tilt the steering wheel in Vertical direction only.
The
Tilt mechanism which offers the driver to adjust the steering wheel in
different positions. The grooves in the Column and a Spring Adjusted
Lock Pin is there. The driver just has to release the pin and adjust it
according to his needs. As the name implies, in this mechanism we just
can tilt the steering wheel in Vertical direction only.
Tilt and telescopic steering column
The Next advancement in Adjustable Steering Column is Tilt and Telescopic Steering Column, which offers the driver to tilt the steering wheel as well as retract and extend it according to needs. It is generally a tubular Steering column which slides up and down itself to contract and expand. There are two levers on the steering column assembly, out of which one controls the Tilt and other controls the Contraction and Expansion.
 Today,
steering wheels and columns are power operated, with memory settings
that move them out of the way for easier access, then return them to the
pre-selected position automatically when we are ready to drive. Memory
settings can be programmed for different drivers on some models. These
are highly advanced compared to the adjustable steering wheel options of
the classic car.
Today,
steering wheels and columns are power operated, with memory settings
that move them out of the way for easier access, then return them to the
pre-selected position automatically when we are ready to drive. Memory
settings can be programmed for different drivers on some models. These
are highly advanced compared to the adjustable steering wheel options of
the classic car.
 Electrically
adjustable steering column manufactured by Lemförder Fahrwerktechnik.
The electric motor 3 turns a ball nut via the gears 4 and this engages
with the grooves 5 of the steering tube and shifts it (position 6) in
the longitudinal direction (position 1). To change the height of the
steering wheel (position 2), the same unit tips around the pivot 8 by
means of the rod 7.
Electrically
adjustable steering column manufactured by Lemförder Fahrwerktechnik.
The electric motor 3 turns a ball nut via the gears 4 and this engages
with the grooves 5 of the steering tube and shifts it (position 6) in
the longitudinal direction (position 1). To change the height of the
steering wheel (position 2), the same unit tips around the pivot 8 by
means of the rod 7.
Advantages of tilt able steering wheel
Automatic Garage Door Opening System A garage door opener is a motorized device that opens and closes garage doors. Most are controlled by switches on the garage wall, as well as by remote controls carried in the garage owner's cars, or more rarely, on key chains.
The first garage door opener remote controls were simple and consisted of a simple transmitter (the remote) and receiver which controlled the opener mechanism. The transmitter would transmit on a designated frequency; the receiver would listen for the radio signal, then open or close the garage, depending on the door position.The disadvantage is that, they opened their neighbor’s garage door as well.
The second stage of the wireless garage door opener system consists of remote controls on these systems transmitted a digital code, and the receiver in the garage responded only to that code. The codes were typically set by eight to twelve DIP switches on the receiver and transmitter, so they allowed for 28 = 256 to 212 = 4,096 different codes. As long as neighbors used different codes, they would not open each other's garage doors. The intent of these systems was to avoid interference with nearby garage doors. The problem was that, the attacker would use a code grabber, which has a receiver that captures the remote's digital code and can re transmit that digital code at a later time. To rectify this, multicode systems were developed.
The third stage of garage door opener technology uses a frequency spectrum range between 300-400 MHz and rolling code (code hopping) technology to defeat code grabbers. In addition to transmitting a unique identifier for the remote control, a sequence number and an encrypted message are also sent.


Traffic Jam Assist




 Night vision systems use an infrared sensor typically in the grille to look for warm objects in the roadway. The sensor is a video camera that captures the infrared spectrum just above visible light. The sensor outputs the moving image to a dashboard display. Increasingly, that’s coupled with sophisticated algorithms that detect humans and large animals, and most recently, that sound an alert. This is the case for all night vision technologies.
Night vision systems use an infrared sensor typically in the grille to look for warm objects in the roadway. The sensor is a video camera that captures the infrared spectrum just above visible light. The sensor outputs the moving image to a dashboard display. Increasingly, that’s coupled with sophisticated algorithms that detect humans and large animals, and most recently, that sound an alert. This is the case for all night vision technologies.
Basic components
 Data from the thermal cameras used in passive systems is typically
processed into a black and white image that provides the driver with an
enhanced view of the road ahead.
Data from the thermal cameras used in passive systems is typically
processed into a black and white image that provides the driver with an
enhanced view of the road ahead.




The real advance is the proactive warning, an audible alert and a warning icon in the instrument cluster, or even better in the head-up display.
How do they call it?
AUDI:Audi Night Vision Assistant (A6, A7, A8) uses a segment of its Matrix Beam headlamps to highlight pedestrians in the vehicle’s path. As with other warning systems, the algorithm also detects and highlights people and animals away from the road as well, but only sounds the alert if an object is in harm’s way. It costs $2,300.
BMW Night Vision with Dynamic Light Spot (5 Series, 6 Series, 7 Series, X5, X6, Rolls-Royce Ghost and Wraith) offers a few more features. Once a pedestrian is detected as a hazard, one of the headlamp modules becomes a spotlight that tracks the pedestrian who is in or close to the roadway. For animals, there’s a unique deer-in-the-headlamps function. The spotlight strobes (flashes) slowly and increases frequency as the car gets closer. In the US, the option is called BMW Night Vision with Pedestrian Detection. It costs $2,300 and may require a $900 option, the cold weather package.
Mercedes-Benz: Night View Assist Plus (SL-Class, S-Class) flashes a segment of the headlamp units to warn the pedestrian on the roadway and pinpoint the location for the driver. It costs $2,260.
The sensor module is responsible to sense the raw data and send via sink node to the communication module (base station). The base station further sends the data to processing module (servers in TMC). Where the data receive the raw data and analyzed and synthesized to process the desired information. After fusion prediction the final data will send to base station again for broadcasting to the vehicles. The system have many distributes sensors, which sense a large amount of driving state detection and sensor information data fusion. Through proposed system the road recognition ability will improved and provide more comprehensive information for safe and efficient vehicle driving.

 |
ITS graphical user interface
displaying the Hungarian highway network and its data points
|
Benefits:
- improved journey planning with real-time information
- safe and efficient use of road space
- rapid detection of incidents
- decrease the environmental impacts of traffic by smoothing traffic flow and minimising rapid accelerations and decelerations
Tilt able Steering Wheel
The
tilt steering mechanism allows selection of the steering wheel position
(in the vertical direction) to match the driver’s driving posture. This
type of steering allows the driver to tilt the steering wheel for ease
during entry and exit. This can be done by releasing a lever on the side
of the steering column and moving the wheel into the desired position,
where it locks itself in place.
Steering column is the piece that attaches the steering wheel to the internal steering mechanism of the vehicle.
conventional steering columnThe main disadvantage of having a conventional steering column is that, the steering wheel’s height and angle cannot be adjusted as per the Driver's need.

Tilt and telescopic steering column
The Next advancement in Adjustable Steering Column is Tilt and Telescopic Steering Column, which offers the driver to tilt the steering wheel as well as retract and extend it according to needs. It is generally a tubular Steering column which slides up and down itself to contract and expand. There are two levers on the steering column assembly, out of which one controls the Tilt and other controls the Contraction and Expansion.
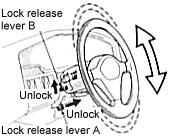
Tilt steering wheel
To change the steering wheel angle, pull up the lock release lever A,
tilt the steering wheel to the desired angle and release the lever.
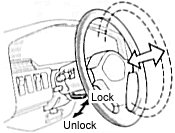
Telescopic steering
column
To
adjust the steering column length, push down the lock release lever,
push or pull the steering wheel to the desired position, and pull the
lever fully up to its original position.

Advantages of tilt able steering wheel
- It helped in driver ergonomics.
- Steering effort is distributed .
- Steering action can now be done at an angle thus driver can be sit comfortably
Automatic Garage Door Opening System A garage door opener is a motorized device that opens and closes garage doors. Most are controlled by switches on the garage wall, as well as by remote controls carried in the garage owner's cars, or more rarely, on key chains.
The first garage door opener remote controls were simple and consisted of a simple transmitter (the remote) and receiver which controlled the opener mechanism. The transmitter would transmit on a designated frequency; the receiver would listen for the radio signal, then open or close the garage, depending on the door position.The disadvantage is that, they opened their neighbor’s garage door as well.
The second stage of the wireless garage door opener system consists of remote controls on these systems transmitted a digital code, and the receiver in the garage responded only to that code. The codes were typically set by eight to twelve DIP switches on the receiver and transmitter, so they allowed for 28 = 256 to 212 = 4,096 different codes. As long as neighbors used different codes, they would not open each other's garage doors. The intent of these systems was to avoid interference with nearby garage doors. The problem was that, the attacker would use a code grabber, which has a receiver that captures the remote's digital code and can re transmit that digital code at a later time. To rectify this, multicode systems were developed.
The third stage of garage door opener technology uses a frequency spectrum range between 300-400 MHz and rolling code (code hopping) technology to defeat code grabbers. In addition to transmitting a unique identifier for the remote control, a sequence number and an encrypted message are also sent.


There are five types of garage door openers:
- Chain drive openers have a chain (similar to a bicycle's) that connects the trolley to the motor.
- Belt drive openers use a rubber belt in place of a chain.
- Screw drive openers have a long screw inside the track. The trolley connects to this screw.
- Jackshaft openers mount on the wall at either end of the torsion bar.
- Direct drive openers have the motor installed inside the trolley and use a gear wheel to guide the trolley along a fixed chain.The typical electric garage door opener consists of a power unit that contains the electric motor. The power unit attaches to a track. A trolley connected to an arm that attaches to the top of the garage door slides back and forth on the track, thus opening and closing the garage door. The trolley is pulled along the track by a chain, belt, or screw that turns when the motor is operated.
 |
| Direct drive |
 |
| operator |
 | |
Traffic Jam Assist

It uses systems such as ACC adaptive cruise control and lane departure warning to allow easy slow driving in traffic jams. The car will follow the vehicle ahead and automatically operate the accelerator and brakes within the limits of the system so the vehicle is kept in lane. Traffic jam assist helps drivers arrive more relaxed at their destination, even in dense traffic or in traffic jams. As a partially automated comfort function, the system takes over the longitudinal and lateral guidance of the vehicle. This means that the car can drive off, accelerate and brake automatically, as well as steer the vehicle.


The system
uses the radar and ultrasound sensors as well as the front camera, guiding the
car by gently adjusting the steering and following the traffic ahead within
system limits. In doing so, the traffic-jam assist uses the lane markings and
other vehicles on the road for orientation.



Dual-Zone Climate Control


Adaptive Highbeam Assist eliminates the need to flip between high and low beams while also ensuring the path ahead is fully lit without ever straining the eyes of other drivers. As other cars approach, the headlamp range automatically adjusts based on the distance of oncoming traffic. Rather than going from one extreme to the other when flipping between high and low beams, Adaptive Highbeam Assist gradually adjusts its headlight range to better light the way without impeding the vision of drivers going the other direction.


The range of the variably adjustable headlamps is set accordingly and adjusted continuously according to the distance of the vehicle ahead or oncoming traffic.The system is extremely fast, relaying fresh data to the headlamps every 40 milliseconds. On the basis of this information, the headlamps are switched to low beam and the range of the adjustable bi-xenon headlamps in dipped-beam mode is set within a maximum reach of 300 metres and continuously adapted to the prevailing traffic situation.

Adaptive headlights

Adaptive headlights are an active safety feature designed to make driving at night or in low-light conditions safer by increasing visibility around curves and over hills. When driving around a bend in the road, standard headlights continue to shine straight ahead, illuminating the side of the road and leaving the road ahead of the car in the dark. Adaptive headlights, on the other hand, turn their beams according to the steering input so that the vehicle’s actual path is lit up. Similarly, when a vehicle with standard headlights crests a hill, the headlight beams temporarily point upwards towards the sky. This makes it difficult for drivers to see the road ahead and for oncoming motorists to see the driver approaching. In contrast, adaptive headlights use a self-levelling system that points the light beam up or down, according to the position of the vehicle.

Most adaptive headlight setups also include a self-levelling system. This system helps prevent headlights from pointing too far up or too far down when driving up or down hills. A self-levelling system includes a level sensor that sends information to the ECU about the vehicle’s position, specifically whether it is tilted forward or backwards. The headlights are then moved up or down to correct for the vehicle’s positioning. Some headlamps are integrated with Adaptive Highbeam Assist which eliminates the need to flip between high and low beams while also ensuring the path ahead is fully lit without ever straining the eyes of other drivers. As other cars approach, the headlamp range automatically adjusts based on the distance of oncoming traffic. The another feature of AHL is the adverse weather light which creates a wider dispersion of the light to improve visibility in rain, fog, or snow. This feature also reduces far-field illumination to minimise reflective glare affecting the driver’s own vehicle.
Cars with AHL:Ford S-Max, Nissan GT-R, Tesla- Model S, Hyundai Genesis, Subaru Outback..etc
Automotive night vision:
Automatic Climate
Control

Automatic climate control is the ability to monitor and influence the temperature of a specified space without manual intervention. This climate control capability can be found in many cars, boats, and airplanes. Its primary purpose is to manage the temperature of a given area based on settings by a user of the system.
The Automatic Climate Control system is the most advanced of all the air conditioning systems in cars. It automatically controls the cabin temperature, air-flow, air distribution, fan speed, air circulation and humidity levels inside the cabin. In Climate Control, we can set the cabin temperature of our choice. However, the system controls it regardless of the outside air temperature and humidity. Some advanced systems offer Dual-zone climate control with automatic re-circulation mode.
The mechanics of automated climate control require sensors to be placed into the compartment of the area to be managed. These sensors read the current temperature of the area. The readings are then matched to the setting defined by the occupants through the computer system within the vehicle, and the heating and cooling are adjusted.
The Automatic Climate Control system is the most advanced of all the air conditioning systems in cars. It automatically controls the cabin temperature, air-flow, air distribution, fan speed, air circulation and humidity levels inside the cabin. In Climate Control, we can set the cabin temperature of our choice. However, the system controls it regardless of the outside air temperature and humidity. Some advanced systems offer Dual-zone climate control with automatic re-circulation mode.
The mechanics of automated climate control require sensors to be placed into the compartment of the area to be managed. These sensors read the current temperature of the area. The readings are then matched to the setting defined by the occupants through the computer system within the vehicle, and the heating and cooling are adjusted.
Cabin Air Temperature Sensors

Automotive
air conditioning systems use NTC sensors to monitor air temperature.
The In Car Temperature sensor (ICTS) is an NTC that monitors the air
temperature of the passenger compartment. The ambient temperature sensor
(ATS) monitors the air temperature outside of the vehicle.
Vent/Outlet Temperature SensorsThese
sensors are located in the vents, just before the air enters the main
cabin. These sensors tell the HVAC system what temperature as well as
what vent air is coming out. This allows the system to find the exact
location of the blend door to provide the exact temperature required.
They also act as a diagnostic device for the system, if air is coming
out of the wrong vent or if the system can’t get the desired
temperature, it will set a fault code. These codes may be part of the
OBD system or they may need to be extracted from the HVAC controls
themselves.
Dual-Zone Climate Control

Dual-zone automatic climate control is when two separate sections of the vehicle can maintain different preferred temperatures autonomously. Usually this means the driver and the front passenger can both choose a temperature that works for them. In some larger vehicles, this might mean that the front seats and the back seats both have independent automatic temperature controls for the heating and the air conditioning.

Cars with dual zone Acura RDX, Toyota Prius, Honda Odyssey, Hyundai Sonata
Adaptive
Highbeam:
Adaptive Highbeam Assist eliminates the need to flip between high and low beams while also ensuring the path ahead is fully lit without ever straining the eyes of other drivers. As other cars approach, the headlamp range automatically adjusts based on the distance of oncoming traffic. Rather than going from one extreme to the other when flipping between high and low beams, Adaptive Highbeam Assist gradually adjusts its headlight range to better light the way without impeding the vision of drivers going the other direction.

Adaptive Highbeam Assist makes night-time driving even safer. The system adjusts the headlamp range automatically to the distance of oncoming traffic or vehicles in front with their lights on. This provides the driver with the ideal headlamp range at all times, enabling better and earlier recognition of the course of the road, pedestrians or other dangers.
The Adaptive Highbeam Assist is based on a camera on the inside of the front windscreen which monitors the traffic situation in front of the car. An intelligent image processing algorithm enables the camera to identify other vehicles and to calculate their distances.

The adjustment of the possible headlamp range is based on controlling the dazzle levels for other road users. This avoids irritating glare, and at the same time offers the maximum low beam light distribution.When the system detects that the road ahead is clear, high beam is activated automatically. Adaptive Highbeam Assist in Mercedes-Benz cars is available at speeds of 55 km/h and over. Once it has been switched on it operates fully automatically.

Mercedes-Benz's
Intelligent Light System increases headlamp range by 50 metres when
driving on the motorway will combine this new development with the
Intelligent Light System, which offers five different bi-xenon light functions,
each of which is suited to typical driving or weather conditions.
- Country mode
- Motorway mode
- Enhanced fog lamps
- Active light function
- Cornering light function
Adaptive headlights

Adaptive headlights are an active safety feature designed to make driving at night or in low-light conditions safer by increasing visibility around curves and over hills. When driving around a bend in the road, standard headlights continue to shine straight ahead, illuminating the side of the road and leaving the road ahead of the car in the dark. Adaptive headlights, on the other hand, turn their beams according to the steering input so that the vehicle’s actual path is lit up. Similarly, when a vehicle with standard headlights crests a hill, the headlight beams temporarily point upwards towards the sky. This makes it difficult for drivers to see the road ahead and for oncoming motorists to see the driver approaching. In contrast, adaptive headlights use a self-levelling system that points the light beam up or down, according to the position of the vehicle.
Adaptive
headlight systems are made up of several sub components that are
monitored and controlled by an electronic control unit (ECU). The sub
components include:
- wheel speed sensors that monitor the speed of rotation of each wheel
- a yaw sensor that tracks a vehicle’s side-to-side movement, e.g., when turning a corner
- a steering input sensor that monitors the angle of the steering wheel and
- small motors attached to each headlight.
- Level Sensor– Sends the information about the vehicle’s position to the ECU
- Rain Sensor System- This sensor is fitted to the vehicle and the data is fetched via CAN network.
- ECU– This is the brain and considers all sensors information for generating the required illumination of lights.

Most adaptive headlight setups also include a self-levelling system. This system helps prevent headlights from pointing too far up or too far down when driving up or down hills. A self-levelling system includes a level sensor that sends information to the ECU about the vehicle’s position, specifically whether it is tilted forward or backwards. The headlights are then moved up or down to correct for the vehicle’s positioning. Some headlamps are integrated with Adaptive Highbeam Assist which eliminates the need to flip between high and low beams while also ensuring the path ahead is fully lit without ever straining the eyes of other drivers. As other cars approach, the headlamp range automatically adjusts based on the distance of oncoming traffic. The another feature of AHL is the adverse weather light which creates a wider dispersion of the light to improve visibility in rain, fog, or snow. This feature also reduces far-field illumination to minimise reflective glare affecting the driver’s own vehicle.
An automotive night vision system uses a thermographic camera to increase a driver's perception and seeing distance in darkness or poor weather beyond the reach of the vehicle's headlights.The technology was first introduced in the year 2000 on the Cadillac Deville. This technology is based on the night vision devices (NVD), which generally denotes any electronically enhanced optical devices operate in three modes: image enhancement, thermal imaging, and active illumination. The automotive night vision system is a combination of NVDs such as infrared cameras, GPS, Lidar, and Radar, among others to sense and detect objects.
1)passive night vision system


Basic components
- Dual camera
- Amplifier
- On board display
- Caution ICU
- Intelligent night vision system
- Motion detection sensor
- Vehicle Speed Sensor
- Daylight Sensors
- Night Vision Sensor
 Data from the thermal cameras used in passive systems is typically
processed into a black and white image that provides the driver with an
enhanced view of the road ahead.
Data from the thermal cameras used in passive systems is typically
processed into a black and white image that provides the driver with an
enhanced view of the road ahead. 
It measure the heat generated by living objects without the need for additional illumination. Warmer objects show up as lighter images on the car’s LCD display, colder objects show up as dark. In between dark grays are the road and rocks emitting heat from the sun into the evening hours.
Due to the reliance on heat emissions, passive systems tend to work
very well with people, animals, and other vehicles, since they all emit a
lot of thermal radiation.
The drawback of passive systems is that they have trouble picking up
inanimate objects that are about the same temperature as the surrounding
environment.
Passive night vision wins hands down for claimed range, up to 1,000 feet or 300 meters. (At 60 mph on a country road, that’s theoretically more than 10 seconds of travel time.) Passive systems work better in rainy and foggy conditions. Passive systems work less effectively at warmer temperatures.


2)Active
night vision system:
Active systems are more complex than passive systems because they use infrared light sources. Since the infrared band falls outside the visible spectrum, these light sources don’t cause oncoming drivers to suffer from temporary night blindness like high beam headlights can. That allows the infrared lights to illuminate objects that are significantly further away than headlights are able to reach.Active night vision systems use an
infrared illuminator, sometimes part of the headlamp cluster, to light up the
road in the IR spectrum. The image can be higher-resolution than passive. Roads
and buildings show up better.

As with normal headlamps, the range of active night vision systems is reduced in rain, snow or fog, and effectiveness falls off with the square of the distance. The biggest drawback with active NV is range, an estimated 500-650 feet or 150-200 meters.
Cars with ANVS: Lexus LX 470 (windshield), LS (instrument cluster), Mercedes-Benz CL-Class, (C216)(instrument cluster)..etc
Auto detection and alerting
Auto detection and alerting
The real advance is the proactive warning, an audible alert and a warning icon in the instrument cluster, or even better in the head-up display.
How do they call it?
AUDI:Audi Night Vision Assistant (A6, A7, A8) uses a segment of its Matrix Beam headlamps to highlight pedestrians in the vehicle’s path. As with other warning systems, the algorithm also detects and highlights people and animals away from the road as well, but only sounds the alert if an object is in harm’s way. It costs $2,300.
BMW Night Vision with Dynamic Light Spot (5 Series, 6 Series, 7 Series, X5, X6, Rolls-Royce Ghost and Wraith) offers a few more features. Once a pedestrian is detected as a hazard, one of the headlamp modules becomes a spotlight that tracks the pedestrian who is in or close to the roadway. For animals, there’s a unique deer-in-the-headlamps function. The spotlight strobes (flashes) slowly and increases frequency as the car gets closer. In the US, the option is called BMW Night Vision with Pedestrian Detection. It costs $2,300 and may require a $900 option, the cold weather package.
Mercedes-Benz: Night View Assist Plus (SL-Class, S-Class) flashes a segment of the headlamp units to warn the pedestrian on the roadway and pinpoint the location for the driver. It costs $2,260.





Auto air conditioning near me
ReplyDelete| Auto air conditioning repair
| Auto air conditioning
You don’t have to suffer through a scorching summer without a properly working car A/C – let our professional technicians perform a proper diagnostic and get you cruisin’ in the cool breeze again!
Having problems with your vehicle? Well worry no more because we are here to help. At Bullitt Automotive we love cars and we love helping our customers. Do you hate pouring all that money into your fuel tank? Nobody does. Here are some services we provide to help your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently. Regular Air filter cleaning is extremely important. A dirty filter greatly reduces your vehicles efficiency.
https://www.bullittautomotive.com/air-conditioning/
Email - service@bullittautomotive.com
Call at - 480-446-0484
Wow :)
ReplyDeleteThis is an incredible collection of ideas!
Waiting for more helpful pieces.
You would amazing to read a similar one here-
bestvacuuming blog
Summer means Car AC goes down I am also car mechanic and write reasons due car AC does not work in hot
ReplyDelete